Easily create wonderful color palettes
To help choose your color palettes, use coolors.co or alternatively Adobe’s color picker.
Color Models
There are three color models commonly used by digital artists:
Note that all these color models are in the RGB color space.
RGB Color Model
RGB stands for Red, Blue, Green. An example of an RGB value is: 16,139,216. Every number group represents one color channel, 139 being the blue channel. Every color channel can range from 0-255. The amount of RGB colors are capped at 16777216.
When to use Use is for quick color picking, colors that won’t be final. Using RGB color model should be avoided, because it’s very hard to select harmonious colors
HSV & HSL Color Model
HSV stands for Hue, Saturation, Value whereas HSL stands for Hue, Saturation, Lightness. The difference being that a color with maximum tint (lightness) is white with HSL and the actual color in HSV.
HSL Example:
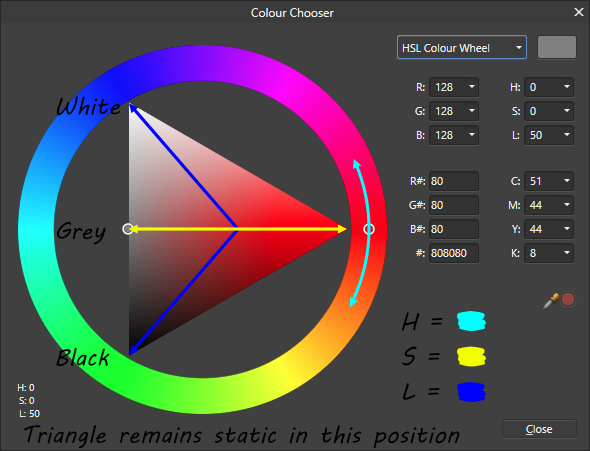
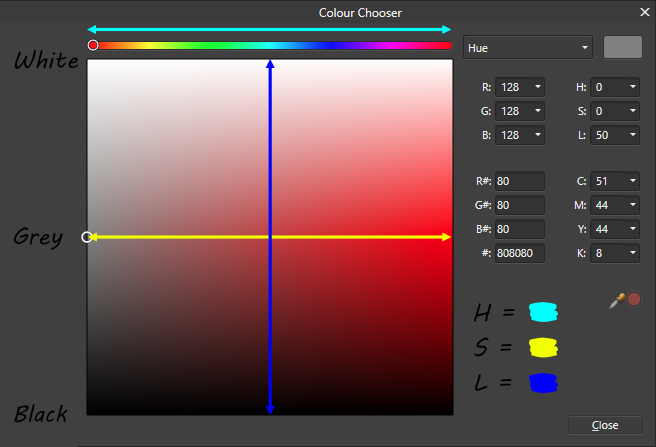
When to use For 2D art and hand painted textures, this is pretty much always the best choice, because of being able to easily select different tints/shades of a color. But it’s also good for any other color picking. The choice between HSV vs. HSL is a thing of preference, though HSV is probably the more popular one.
Hex Color Model
A hex color is like RGB. The syntax is #RRGGBB, so green would be #00FF00. 00 means none of that channel and FF means 255 of that channel (0-9, A-F). It’s also possible to store alpha in hex with the following syntax #RRGGBBAA, so green with alpha would be #00FF0012. The “A” can only range from 0-100.
When to use HEX is almost only used for copying a color per values from A to B
Color Theory Glossary
| Keyword | What is it | What does it affect | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tint | Mixture of a color with WHITE | Lightens the color & increases the color’s brightness | |
| Shade | Mixture of a color with BLACK | Darkens the color & decreases the color’s brightness | |
| Tone | Mixture of a color with GRAY | ||
| - | - | - | |
| Hue | Pure Colors(Primary Colors, Secondary Colors, …). Ranges from 0° to 359° on the color wheel | Changing the Tint, Shade or Tone of a color doesn’t change the hue | |
| Saturation | |||
| Value | Tint(lightness) and Shade(darkness) of a color | ||
| Chroma / Chromatic Intensity | A color where a hue predominates, blue, green, while white gray and black are achromatic because no hue predominates. |
| Keyword | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Primary Color | 3 in total. Source of all colors (Red, Blue and Yellow) |
| Secondary Color | 3 in total. Made of equal amount of 2 primary colors. Located between primary colors (Red + Yellow = Orange; Red + Blue = Violet/Purple; Blue + Yellow = Green) |
| Tertiary Color | Made by mixing a primary color with one secondary color |
| Warm Colors | Energy, Joy, passion, enthusiasm |
| Cold Colors | Calmness, peace, professional |
| Active Colors | |
| Passive Colors | |
| Additive Colors | |
| Subtractive Colors | |
| Dominant Color | |
| Recessive | Fades into the background |
| Balanced | |
| Unbalanced | |
| Monotony |
Color Synergy
Colors which, when combined or mixed, cancel each other out or boost a one of the colors. One of the things it’s used for is to make things stand out.
Official Synergy Types
A great place to create these synergies and understand how they work is Adobe’s color picker.
Complementary
- Dark Purple - Yellow, Lime Green - Light Purple
Split complementary colors
Analogous colors
Triadic colors
Tetradic or double complementary colors
Monotone chromatic
- Uses a single hue and all its tints, tones and shades
- Risk of monotony
Monotone achromatic
- Only neutral colors ranging from black to white
- Is monotone
Common Colors RGB & HEX
| COLOR | RGB | HEX |
|---|---|---|
| White | 255,255,255 | #FFFFFF |
| Black | 0,0,0 | #000000 |
| Neutral Gray (50%) | 127.5,127.5,127.5 | #7F7F7F |
| Red | 255,0,0 | #FF0000 |
| Lime | 0,255,0 | #00FF00 |
| Blue | 0,0,255 | #0000FF |
| Yellow | 255,255,0 | #FFFF00 |
| Cyan | 0,255,255 | #00FFFF |
| Magenta | 255,0,255 | #FF00FF |
🚧Work in Progress🚧
Hue
- Changing the Tint, Shade or Tone of a color changes the Chroma / Colorfulness
Tint
- Changing the tint also changes the Saturation
Shade
- Changes the Saturation
Tone
- Or produced by both Tinting and Shading (Because white + black is gray)
terms to cover
colorfulness, saturation, purity, intensity, luminance
Saturation
Saturation is changed by tint, shade and tone. Saturation is the purity / intensity / brilliance of a color. The higher the saturation of a color, the more vivid and intense it is. The lower a color’s saturation, the closer it’s to pure gray on the grayscale. Also chroma
Brilliance & Brightness
Brilliance judged relative to the maximum brightness possible, whereas brightness is relative to the brightness of a similarly illuminated white object.